Are Lectins Bad for You? Find Out
Every other day, there seems to be a new trend urging us to eliminate certain foods or food groups to achieve that lean, fit body we all desire. These trends often suggest that one specific food is the only thing standing between you and your dream physique. One such long-standing trend revolves around lectins. But before jumping on the why behind it, let’s take a closer look at the facts, starting with the basics.
What are Lectins?
These are proteins that bind to carbohydrates and can interact with specific sugars in a reversible way. Often referred to as “anti-nutrients,” these can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb and digest nutrients. Essentially, these act as a form of protection for plants, helping them fend off animals, insects, and microorganisms.
Are Lectins Harmful to Humans?
While our bodies cannot digest lectins, they typically pass through the digestive system harmlessly in healthy individuals. However, those with conditions such as Crohn’s disease or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may experience more significant issues, as a compromised gut lining can allow lectins to enter the bloodstream and trigger an immune response. For example, phytohemagglutinin in raw or undercooked kidney beans can cause symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and cramps due to red blood cell clumping.
In healthy individuals, the gut lining repairs minor damage caused by food as it passes through, preventing large molecules from entering the bloodstream. However, when lectins compromise this repair process, it may result in more serious long-term damage, leading to an increase in large molecules crossing into the bloodstream and triggering immune responses. Some research even suggests that these may contribute to autoimmune conditions.
Moreover, these can interfere with the absorption of essential minerals like zinc, calcium, phosphorus, and iron. They may also disrupt the balance of gut microflora by binding to the intestinal lining, affecting nutrient absorption.
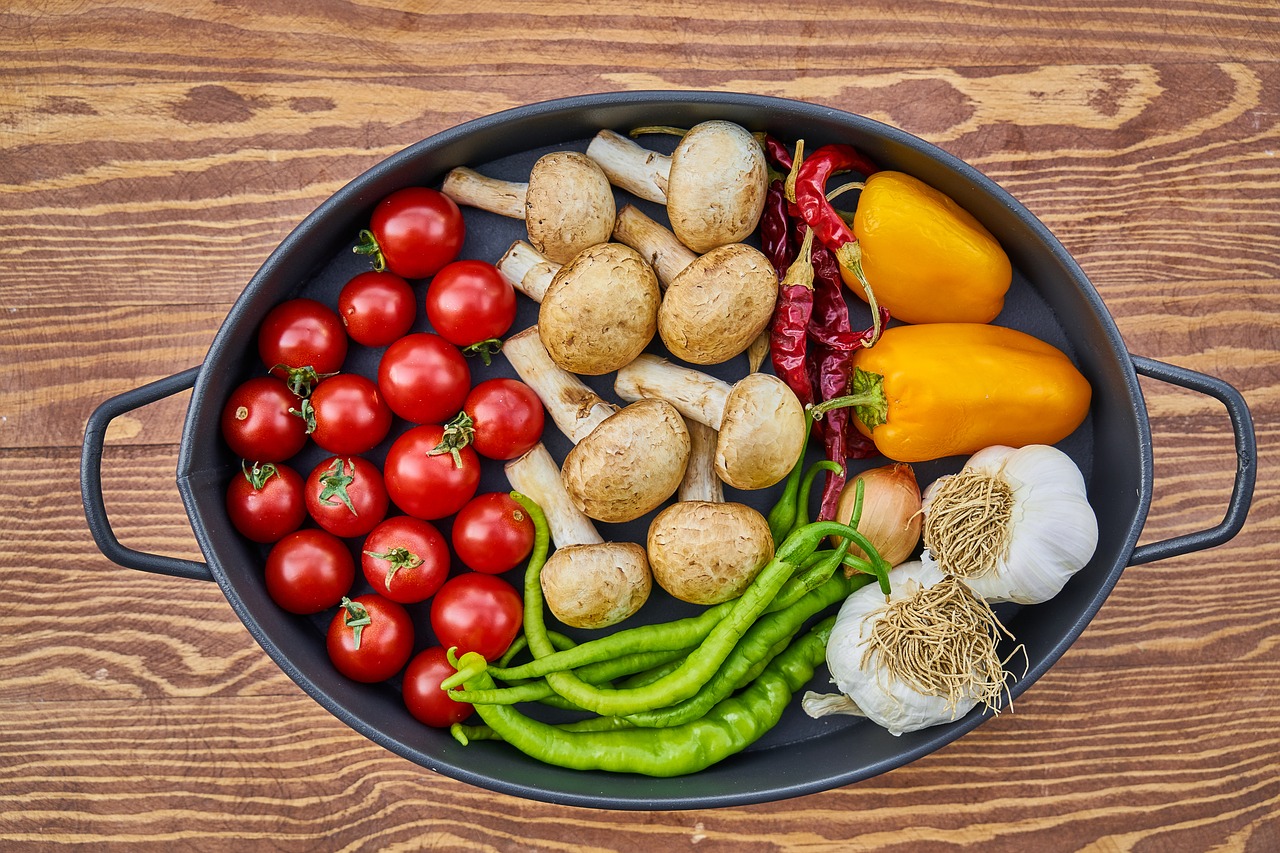
Which Foods Contain Lectins?
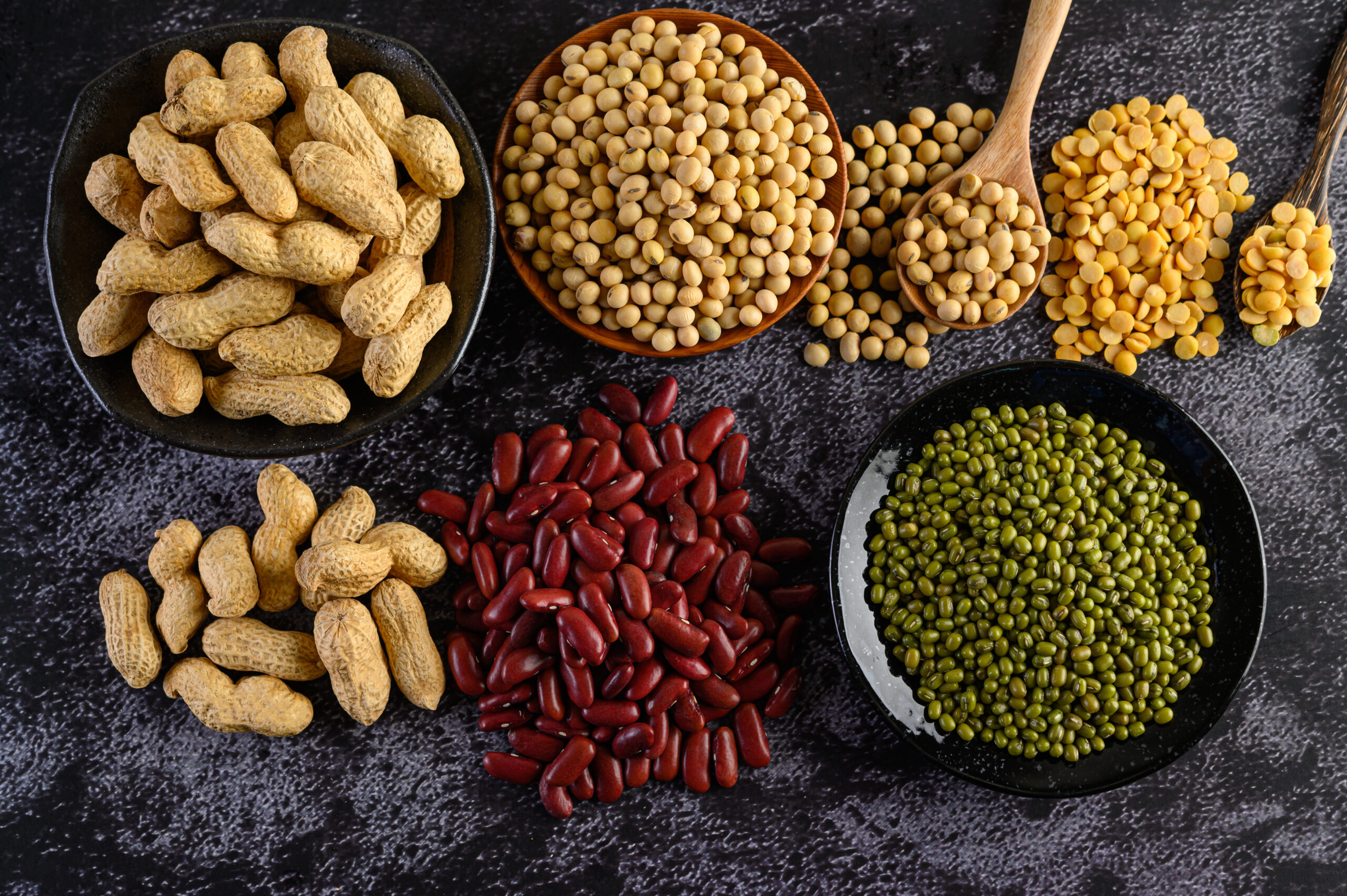

Here are the top 10 foods:
1. Raw kidney beans
2. Soybeans
3. Wheat
4. Peanuts
5. Tomatoes
6. Potatoes
7. Barley
8. Eggplant
9. Lima beans
10. Navy beans
Nightshade vegetables (like eggplant, potatoes, and peppers) and certain grains (like wheat and barley) are also notable sources.
Should We Stop Eating Lectin-Containing Foods?
No! The levels of lectins that are harmful are much higher than what we typically consume in a balanced diet. Plus, there are effective ways to neutralize them during food preparation, which is why how you cook food matters as much as what you eat.
How to Reduce Lectins in Food?
Since lectins are water-soluble and often located on the outer surface of food, rinsing or soaking foods in water can reduce their lectin content. Most lectins are also deactivated by heat, so cooking methods like boiling and steaming make lectin-rich foods safe to eat.
Soaking foods like kidney beans or chickpeas for 24 hours (changing the water every 12 hours) is an effective method to reduce it, making them easier to digest. The same goes for nuts and seeds, which should be soaked for 6-8 hours before consuming to eliminate lectins. Always discard the soaking water and rinse the food before eating.
Another way to reduce it is through sprouting, which dissolves lectins in water and triggers enzymes that break them down. Additionally, peeling or dehulling beans and grains can further reduce their content.
Ever wondered why your mom or grandma insisted on thoroughly washing or soaking grains and pulses? This wisdom is deeply rooted in science, even though we may lose sight of it in the rush of modern life and ready-to-eat foods. Going back to these time-tested methods can improve our health.
Can We Eat Lectins?
For most healthy people with no underlying gut or autoimmune issues, these foods are perfectly fine when prepared correctly. However, individuals with gut sensitivities or autoimmune conditions should be cautious and consult a healthcare professional to determine if specific lectins are causing issues.
Are There Any Benefits to Eating Foods Containing It?
Like most things, lectins aren’t all bad. They can act as antioxidants, protecting the body from free radicals. Because they bind to carbohydrates, they can also help prevent blood sugar spikes after consuming carb-rich foods—an advantage for those managing diabetes.
Lectin-rich foods are also packed with protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats, making them beneficial for those focused on fat loss, heart health, and combating insulin resistance. In addition, some studies suggest that they may contribute to cancer cell death, sparking interest in their potential use in cancer therapies.
The Big Takeaway
Diet trends should never be one-size-fits-all. A personalized approach is always best. For those with gut sensitivities, reducing the intake of these foods may be beneficial, but it’s important to consult with a nutritionist or healthcare professional before making any significant changes.
If you’re healthy, following traditional methods like soaking, sprouting, and cooking your food properly can naturally reduce lectin levels, allowing you to enjoy a nutritious and balanced diet. Before jumping on the next health trend, take a step back, reason, and consult an expert for advice tailored to your specific needs.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.
|
From a pimple to cancer, our You Care Wellness Program helps you find a way Talk to our integrative team of experts today 18001020253 |









Leave a Reply