Why are my ears ringing? It could be Tinnitus.
Do your ears ring without a sound?
Here’s why and what to do
What is Tinnitus, and what are its Statistics?
- The meaning of the word tinnire is “to ring”.
- It is the condition that causes ringing in the ears, or abnormal sounds and sensations.
- The definition of tinnitus is “the perception of noise or ringing in the ears”, or “hearing sounds in the ears when no external sound is present.”
- According to the statistics, tinnitus affects 1 -5 % of the population.
- Nearly 50 million Americans experience it.
- It can affect one ear or both ears.
Symptoms:
| Hearing these sounds, when no sound is coming from an outside source | Phantom sounds | Ringing | Breathing | Clicking |
| Humming | Buzzing | Inside swirling of a seashell | Hissing | |
| Roaring | The sounds of escaping air | Sizing | Heartbeat |
- The sounds can change in their intensity, pitch, onset, volume, and type.
- They can be soft and slow, or loud and fast.
- One can rarely hear musical sounds.
- One can feel disturbed, and may cause psychological and mood-related problems like anxiety, depression, irritability, fatigue, insomnia, or even thoughts of suicide.
- It can interfere with your ability to concentrate.
- It can lead to brain fog, confusion, and trouble with focusing.
- It might also cause problems with speech, especially in children.
Causes or Risk Factors for Tinnitus:
Anything causing an infection or inflammation of the nose, throat, neck, head, or jaw may cause tinnitus as the same nerves are related to the ears.
| · Ear disorders, ear infections, or inflammation.
· Changes in ear bone (otosclerosis). · Eardrum rupture or ear canal obstruction. · Earwax buildup. · Inner ear damage: This changes the way tiny hairs inside the ears move in response to sound waves, causing false electrical signals to be sent through the auditory nerves to your brain. · Headphones and loudspeakers. · Meniere’s disease: A disorder due to fluid accumulation in the inner ear. · Too much shaking of the head. · Due to ageing (called presbycusis). |
· Conditions that affect blood flow, arteries, and the nerves (CVD, BP, Diabetes, Thyroid).
· Upper respiratory infection like a cold. · Arteriosclerosis or hypertension, as hardening of the arteries or high blood pressure cuts off normal blood flow, and affects nerve signals leading to the ears. · Preeclampsia (spike in blood pressure during pregnancy). · Cervical injury. · Vertigo. · Muscle stress or physical fatigue. · Sinus infections, as it causes numbing. · Experiencing jaw, head, or neck injuries (as the same nerves are connected to the ear), also called the TMJ junction. · Migraine or headaches. |
· Cranial nerve tumours affect parts of the brain connected to sound and hearing (acoustic neuroma).
· Anaemia. · Significant weight loss from malnutrition. · Having acute anxiety, insomnia or depression. · Hormonal changes (in women). · Bell’s palsy. · Smoking, neurological changes due to alcohol or drugs. · A rapid change in pressure in the environment like higher altitudes, being in an airplane, and so on. |
Medications that can cause Tinnitus:
- Antibiotics
- Cancer medications
- Water pills (diuretics)
- Quinine medications
- Certain antidepressants
- Aspirin (when taken for 12 or more days)
Foods that can worsen Tinnitus Symptoms:
- Salt, Caffeine: These increase blood pressure, and even restrict blood flow, which may affect blood reaching the ear, eye, and brain.
- Artificial Sweeteners, Sugar (Refined): The inner ear has no energy reserves, and depends on oxygen and glucose from the blood as its energy source. Excess sugar in the blood may affect the glucose and blood reaching the ear affecting the inner ear’s functioning.
- Saturated and Trans Fats: These fats causes inflammation, makes the blood viscous, and reduces blood flow towards the ear.
- Sulfites: These are found as a preservative generally. Avoiding sulfite-containing foods can help control the condition.
- MSG: It is a known flavour enhancer and an excitatory neurotransmitter that increases electrical activity in the brain and auditory cortex. This leads to perceived, loud noises.
- Processed Foods: Junk or fast foods contain all of the above ingredients, so it is highly recommended to avoid them completely.
- Alcohol: Alcohol leads to dehydration affecting the functioning of the inner ear.
- Smoking: Like the brain, the inner ear utilizes oxygen and glucose from the blood for normal functioning. Smoking can affect lung capacity and oxygen uptake, worsening tinnitus.
Nutritional Guidelines to manage Tinnitus:
- Omega 3 fatty acids reduce inflammation. Food rich in omega 3 fatty acids include flaxseeds, fish oil, walnuts, chia seeds, and so on.
- Anti-inflammatory foods like Ceylon cinnamon, garlic, ginger, turmeric, and so on.
- Vitamin B1: Thiamine helps with stabilization of the nervous system. Food sources include outer layers and germ of cereals, as well as in nuts, whole grains, and pulses. Fruit and vegetables containing it include cauliflower, oranges, eggs, potatoes, asparagus, and kale.
- Vitamin B-6 is responsible for serotonin production, a brain neurotransmitter that controls our moods, appetite, sleep patterns, and pain sensitivity. Food sources include bananas, chickpeas, potatoes, and pistachios.
- Potassium: It helps to regulate the flow of fluids throughout the body. Food sources include bananas, spinach, potatoes, mushrooms, and sweet potatoes.
- Pineapple: Pineapples have anti-inflammatory properties. Less swelling in the ears can reduce the intensity of tinnitus.
- Vitamin B12 and Zinc improve nerve health. Food sources include fermented food items like idli, dosa, dhokla, eggs, and so on. Zinc sources are pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, and cruciferous vegetables.
- Magnesium is also excellent for nerves. Food sources include nuts, seeds, cacao, and green leafy vegetables.
Home-Made Ear Drops and Remedies that work Wonders:
The recipe mentioned below is for applying drops in the affected ear using a clean dropper bottle or baby syringe. Cover your ear with a cotton ball or clean cloth, and lean on the opposite side to allow the drops to enter and sit in the ear. Do this for about 5 minutes. In case you feel any uneasiness, flip over to the other side, and let the mixture drain out.
- Holy Basil or Tulsi ear drops: Blend a handful of tulsi leaves, and boil it for 5 minutes in 2 cups water. Reduce it to half, then strain by pressing the extract, and allow it to cool. Using a dropper, you can put 2-3 drops of this in the affected ear.
- Onion juice ear drops: Chop one onion, and boil in 100 ml water. Reduce it to half, cool, strain, and put 2-3 drops of this extracted juice in the affected ear for 5 minutes.
- Garlic- sesame oil ear drops: Sauté garlic in 1 tablespoon of cold-pressed sesame oil. Let it cool. Carefully take the oil (only) and add 2-3 drops to the affected ear (garlic- mustard oil combination also works, but first, try a tiny drop, and observe your tolerance).
- Mustard ear drops: Heat cold-pressed mustard oil, and let it cool. Put 1-2 drops of this oil into the ear.
- Ginger ear drops: Apply warm ginger juice around the outer ear canal (outer application only).
- Olive oil ear drops: Putting a few drops of warm olive oil in the ear helps too.
- Oregano ear drops: Heat 1 tsp of Oregano with 2 tbsp of cold-pressed coconut oil, and leave it overnight. Strain and apply 2-3 drops of this oil in the ear.
- Tea tree oil ear drops: Mix 2-3 drops of tea tree oil with one teaspoon of olive oil, and place 2-3 drops inside the ear.
- Clove – sesame oil ear drops: Sauté 2 cloves in 1 tbsp of cold-pressed sesame oil. Apply 2-3 drops of this inside the ear.
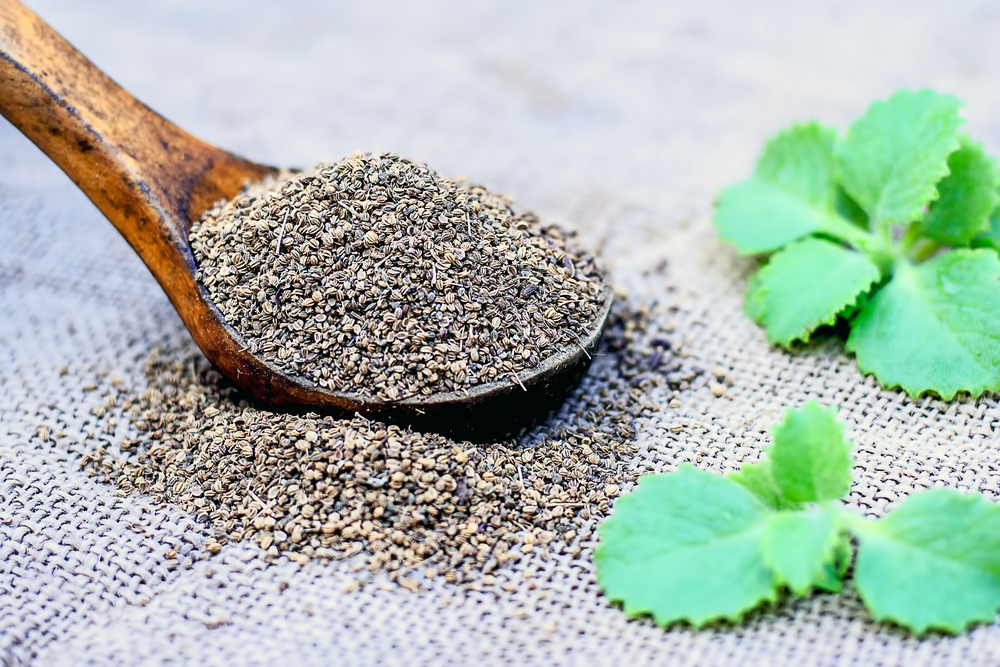
10. Ajwain ear drops: Heat 1 tsp of ajwain with cold-pressed coconut or sesame oil, and leave it overnight. Strain and apply 2-3 drops of this oil in the ear.
11. ACV ear drops: Mix apple cider vinegar with mother + water in 1:3 parts. Apply 3-4 drops in each affected ear.
12. For babies: Dropping a drop of breast milk in each ear helps.
- Neem juice: 2-3 drops of strained neem juice extracted by crushing the leaves, or dip a cotton swab in neem oil, squeeze out the excess, and then place it in your ear for a few minutes before removing it.
- Peeled garlic: Place peeled garlic (big) near the affected ear for 15-20 minutes. Ensure the garlic does not slip into the ear.
- Sleep posture: Sleep with the affected ear raised, instead of having it faced down toward the pillow. This can help the ear drain better if necessary.
- Music therapy: Music and sound therapy also work well.
- Ice or warm compress: Place an ice pack or a warm compress over the ear, and alternate between warm and cold for 10 minutes.
- Sweet almond oil: Take warm sweet almond oil, and massage it in at the point, where your ear joins your cheek. You could also use olive oil or mustard oil instead of almond oil.
- Garlic and ajwain mix: Heat some garlic and ajwain on tawa or pan. Place it in a cloth, and make a warm compress for the ear; this can be done for kids too.
- Hair dry: Use a hairdryer on low to dry the water from the ears after every washing your hair.
Exercises for Tinnitus:
- Exercise 1: Chin to Chest: Sit up straight, and lower your chin to your chest. Intertwine your fingers, and place your joined hands on the back of your head, then pull your head back, while allowing your fingers to arrest the motion. Do not overexert yourself, and repeat this exercise three to five times daily to help relax your spinal cord.
- Exercise 2: Tongue-Tonsils: Open your jaw as wide as possible, and while in this position, touch the roof of your mouth with the tip of your tongue. Move the tip of your tongue backwards towards your tonsils, and hold for a couple of seconds, then stick your tongue out as far as you will be able to, and hold. Repeat this exercise four or five times.
- Exercise 3: Chin moves: Sit up straight, and move your chin upwards and downwards 20 times like in a nodding motion. Imagine you are shaking your head, and move your chin from side to side. Repeat this exercise 3 times, and be mindful that you do not strain your neck.
- Exercise 4: Head up: Sit up straight, and open your jaws wide, but keep them relaxed. As your mouth opens, tilt your head back until you are looking up at the ceiling or sky, inhale deeply, then exhale slowly before returning to the starting position.
- Exercise 5: Snapping:
- Step 1: Cover your ears with your palms, such that the fingers are held on the back of your head, with the middle fingers touching each other.
- Step 2: Ensure your fingers are about one inch above, where your skull meets your neck.
- Step 3: Place your index finger on top of your middle finger, such that they are crossing each other.
- Step 4: Firmly snap the crossed index fingers against the base of the skull. Ensure you are not snapping onto your neck but onto the occiput, the bone at the bottom of the skull. There will be a loud drumming, hollow sound. Repeat the finger-snapping action about 50 times.
- Jaw exercises for tinnitus:
- Max opening: Open your mouth as wide as possible, using your hand. Hold this position for 30 seconds. It is advised not to try this exercise, when feeling acute tinnitus pain. Repeat this exercise 4 times.
- Lateral movement: With your mouth relaxed and slightly open, move your jaw slightly from side to side as far as you will be able to. Next, used a closed fist against your jaw to push it further, either right or left. When applying this extra pressure, hold each option for 30 seconds. Repeat 4 times in four daily sessions.
Yoga for Tinnitus:
- Janu Sirsasana (head-to-knee pose)
- Baddha Konasana (bound angle pose)
- Supta-Vakrasana (Recline twist)
- Jalneti+ Karna Randra Dhouti+ Kapal Randra Dhouti
- Neck Rotations
Final Thoughts:
The ‘ringing of the ears” (tinnitus) feels like torture, and this noise may affect sleep patterns, and the ability to function normally. There is no right or wrong for tinnitus relief, but it is important to know that you are not powerless. The ability to change your feelings and reactions about tinnitus can be the most potent method for managing your tinnitus.
Engage in lifestyle and wellness activities to improve the perceived intensity of tinnitus:
- Mindfulness Meditation
- Good sleep hygiene
- Yoga
- Good physical activity
- Using natural ear drops
- Inculcating good food habits
- Managing stress and anxiety
Disclaimer: None of what is shared above is a replacement for your current medication. If some remedy does not suit you, please do not do it.
|
From a pimple to cancer, our You Care Wellness Program helps you find a way Talk to our integrative team of experts today 18001020253 |







Leave a Reply